PART AND ASSEMBLY DESIGN
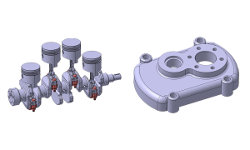
Our expertise extends to both part design and assembly design, allowing us to deliver comprehensive and precise solutions. With our in-depth knowledge of Catia V5's tools and features, we can efficiently develop intricate part models with accurate dimensions and complex geometries. Furthermore, our proficiency in assembly design ensures seamless integration of components, optimizing functionality and manufacturability.
SKELETON METHOD
In CATIA V5, the "Skeleton Method" refers to a technique used to create a framework or reference structure that serves as a basis for designing complex assemblies. It allows you to establish relationships between various components, define their spatial positions, and capture design intent.
The Skeleton Method involves creating a skeleton model, also known as a "Master Model" or "Reference Model," which acts as a foundation for the assembly. The skeleton model contains key features, parameters, and constraints that define the overall architecture and behaviour of the assembly. It provides a flexible and efficient way to manage changes and updates across multiple components.
The Skeleton Method in CATIA V5 enables designers to build complex assemblies by providing a centralized and controlled approach to design. It helps streamline the design process, facilitates design modifications, and promotes consistent design intent throughout the assembly.
AIRBUS RULES AND GUIDELINES
Airbus has specific modeling rules and guidelines when it comes to 3D modeling in Catia V5. These rules ensure consistency, standardization, and compatibility throughout the design and manufacturing process. Some of the key modeling rules followed by Airbus in Catia V5 include:
1. Part Design: The part models should adhere to the defined material thicknesses, curvature requirements, and tolerances. The use of specific drafting standards and naming conventions is essential for clarity and traceability.
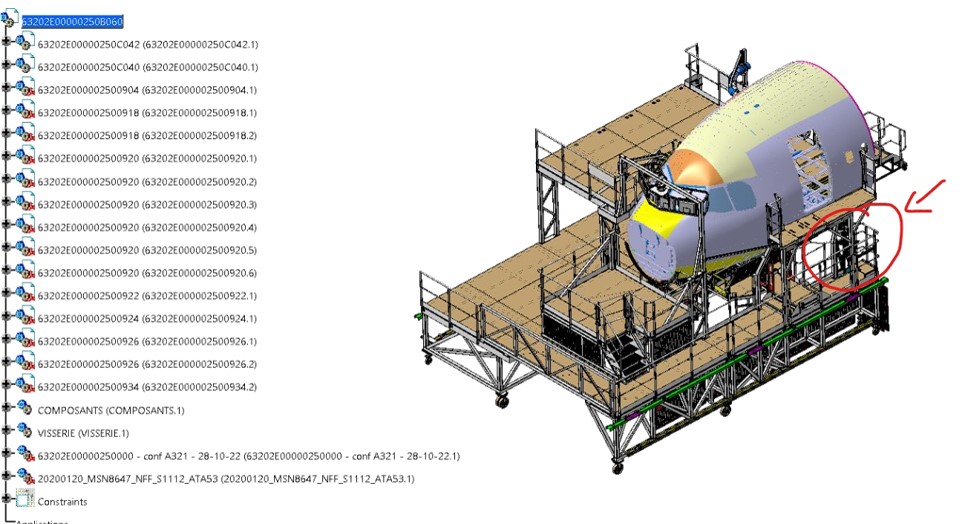
2. Assembly Design: Components within an assembly should be accurately positioned and constrained, ensuring proper fit and functionality. The assembly structure should follow a logical hierarchy, with appropriate naming conventions for easy identification and management.
3. Design Intent: The models should capture the design intent accurately, representing the desired form, fit, and function. Proper dimensioning, geometric constraints, and feature dependencies are critical for maintaining the intended design behavior.
4. Design for Manufacturability: The models should consider manufacturing constraints, such as tooling limitations, material properties, and assembly processes. Design features should be optimized for cost, weight, and ease of production.
5. Data Exchange and Collaboration: Airbus emphasizes the use of standardized file formats and data exchange protocols for effective collaboration within the supply chain. Compliance with specific file naming, organization, and metadata requirements is crucial for seamless integration.
Our company possesses extensive experience in adhering to Airbus rules and guidelines within Catia v5, ensuring seamless collaboration and compliance..